The Complete Guide to Compliance Documentation Lifecycle Management: From Creation to Audit-Ready Archival
THIS BLOG WAS WRITTEN BY THE COMPLIANCE & RISKS MARKETING TEAM TO INFORM AND ENGAGE. HOWEVER, COMPLEX REGULATORY QUESTIONS REQUIRE SPECIALIST KNOWLEDGE. TO GET ACCURATE, EXPERT ANSWERS, PLEASE CLICK “ASK AN EXPERT.”
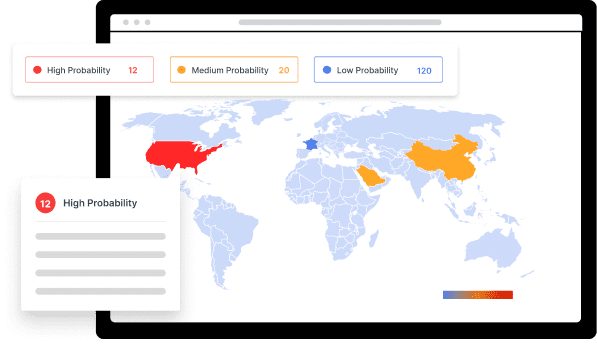
Managing regulatory documentation isn’t just about storage – it’s about survival in an increasingly complex compliance landscape. With organizations facing over $300 billion in fines annually due to inadequate document practices, the need for systematic Compliance Documentation Lifecycle Management (CDLM) has never been more critical.
This comprehensive guide explores every stage of the compliance documentation journey, from initial authoring through long-term digital preservation. You’ll discover proven strategies for version control, metadata optimization, validation protocols, and audit readiness that transform documentation from a compliance burden into a strategic advantage.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Compliance Documentation Lifecycle Management
- Why CDLM Matters More Than Ever
- The Five Critical Phases of CDLM
- Evaluating CDLM Solutions
- Building Your Implementation Strategy
- FAQ: Common CDLM Challenges
Understanding Compliance Documentation Lifecycle Management
Compliance Documentation Lifecycle Management encompasses the systematic approach to creating, maintaining, and preserving regulatory documents throughout their entire operational lifespan. Unlike traditional document management, CDLM addresses the unique requirements of regulated industries where documentation serves as evidence of compliance, risk mitigation, and operational excellence.
The lifecycle spans five interconnected phases: creation and authoring with standardized templates and approval workflows, metadata assignment that transforms documents into searchable assets, storage and access management balancing security with accessibility, retention and archival for long-term preservation, and validation protocols that support audit readiness. Each phase presents distinct challenges, and failures in any single area can compromise your entire compliance posture.
Why CDLM Matters More Than Ever
The financial stakes surrounding compliance documentation have reached unprecedented levels. Poor document management practices contribute to approximately 21% of organizational productivity loss, with employees spending up to 30% of their time searching for documents. More troubling, 86% admit to recreating documents they cannot locate – a significant compliance risk in regulated environments.
The cost of non-compliance extends far beyond direct fines. Inadequate data and document practices increase the average cost of a data breach by approximately $220,000, with highly non-compliant organizations facing costs as high as $5.05 million. This represents a 12.6% premium over organizations with mature compliance practices.
Version control failures present particularly acute risks. Research indicates that 83% of employees struggle with version control issues, while 95% report difficulty locating the most current document versions. In regulated environments, submitting outdated documentation or operating from superseded procedures can trigger immediate regulatory action.
Forward-looking organizations recognize CDLM as a competitive differentiator rather than merely a compliance cost center. Companies with advanced documentation practices can accelerate product launches, streamline audit processes, and demonstrate regulatory readiness that builds stakeholder confidence.
The Five Critical Phases of CDLM
Phase 1: Document Creation and Version Control
The document creation phase establishes the foundation for all subsequent lifecycle activities. Effective CDLM begins with standardized document templates that embed regulatory requirements directly into the authoring process. For FDA-regulated organizations, templates must accommodate 21 CFR Part 11 requirements including electronic signature capabilities, audit trails, and user authentication.
Version control represents one of the most critical yet commonly mismanaged aspects of compliance documentation. Effective strategies begin with standardized naming conventions that embed metadata directly into file names, providing immediate context about document status, approval level, and relevant dates. For example: [DocumentType][ProductID]v[Major.Minor][Status][Date].
Automated numbering systems prevent conflicts while ensuring consistent progression through revision cycles. These systems should integrate with approval workflows to prevent unauthorized version creation and maintain clear lineage between document iterations. Check-in and check-out procedures prevent simultaneous editing conflicts while maintaining comprehensive records of document custody.
Phase 2: Strategic Metadata Tagging
Metadata transforms compliance documents from static files into intelligent assets that support both human decision-making and automated processes. Strategic metadata implementation enables instant document discovery, automated compliance reporting, and predictive analytics that identify potential issues before they become regulatory problems.
Effective metadata strategies begin with comprehensive taxonomies that capture regulatory relevance, operational context, and business relationships. Dublin Core provides a foundational framework that many organizations adapt for compliance purposes, with industry-specific extensions addressing particular needs. Pharmaceutical companies might add elements for drug substance and clinical phase, while manufacturing organizations include product line and safety classification.
AI-powered auto-tagging can automate significant portions of the metadata assignment process while maintaining accuracy levels that exceed manual tagging. Natural language processing enables automatic extraction of regulatory references and compliance concepts from document text. Training data quality directly impacts accuracy, but organizations that implement systematic feedback loops typically see tagging accuracy improve significantly within the first year.
Phase 3: Secure Storage and Access Management
Storage and access management creates the operational foundation that enables daily compliance activities while maintaining security and audit readiness. The choice between cloud and on-premise deployment significantly impacts security posture, operational flexibility, and total cost of ownership.
Cloud deployment offers compelling advantages including automatic security updates, scalable infrastructure, and reduced IT overhead. Major providers maintain compliance certifications for SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GxP requirements. However, some regulatory frameworks impose specific geographic restrictions on data storage or require direct organizational control over security configurations. Hybrid approaches increasingly provide optimal balance.
Role-based access controls balance operational efficiency with security principles including least privilege access and separation of duties. Functional roles typically align with document lifecycle phases, ensuring individuals can access materials relevant to their responsibilities without exposing sensitive information unnecessarily. Regular access reviews ensure permissions remain aligned with current roles and responsibilities.
Comprehensive audit trails provide the foundation for demonstrating compliance with regulatory oversight requirements. User activity logging must record all document interactions including access events, modifications, downloads, and sharing activities, capturing user identity, timestamp, action performed, and relevant context.
Phase 4: Long-Term Digital Preservation
Long-term preservation addresses the complex challenge of maintaining document accessibility and integrity over retention periods that may span decades. Digital preservation begins with format selection decisions that balance current operational requirements with long-term accessibility goals.
Open standard formats generally provide superior long-term preservation characteristics. PDF/A formats specifically address archival requirements through standardized feature sets and embedded font requirements that ensure consistent rendering across different systems and time periods.
Format migration strategies require systematic planning that addresses both technical conversion requirements and validation procedures ensuring migrated documents maintain fidelity to original content. Migration planning should identify trigger events including vendor discontinuation announcements, operating system compatibility issues, or periodic format assessments.
Comprehensive backup strategies ensure document availability throughout extended retention periods. Geographic distribution protects against localized disasters while cloud-based backup solutions increasingly provide cost-effective replication with automated recovery capabilities. Recovery testing validates backup integrity through regular exercises that identify potential issues before they impact operations.
Phase 5: Validation and Audit Readiness
Validation protocols transform compliance documentation systems from passive repositories into active compliance tools that demonstrate regulatory adherence through systematic evidence compilation and reporting.
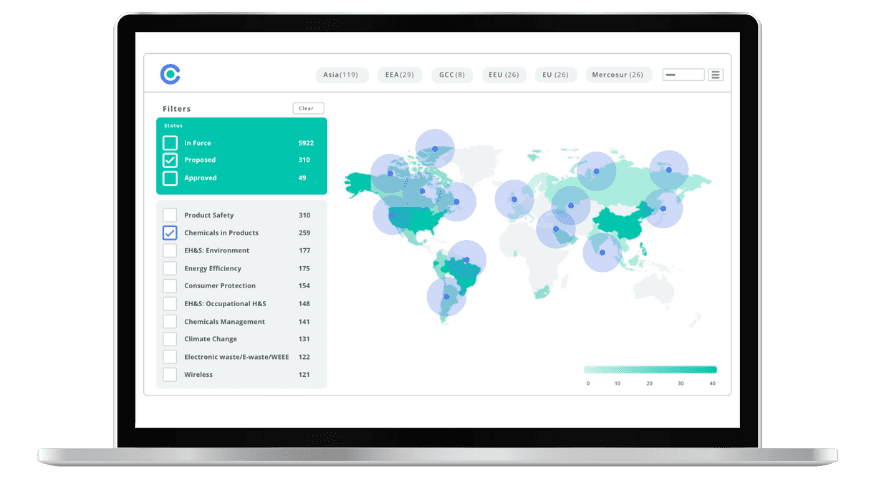
Audit preparation begins long before auditor arrival through systematic evidence compilation that ensures document systems can efficiently respond to regulatory inquiries. Document inventories provide comprehensive catalogs organized by regulatory framework, business process, and compliance requirement. Traceability mapping demonstrates relationships between documents, business processes, and regulatory requirements through visual representations that auditors can easily understand.
Mock audit exercises test system responsiveness and staff preparedness through simulated auditor requests and timeline pressures. These exercises identify potential bottlenecks, knowledge gaps, and procedural issues that can be addressed before actual audits occur.
Automated reporting transforms compliance documentation systems into proactive compliance tools. Compliance dashboards provide real-time visibility into document status, approval bottlenecks, and emerging compliance risks. Exception reporting automatically identifies situations requiring management attention including overdue documents, missing approvals, and policy violations.
Evaluating CDLM Solutions
Selecting appropriate CDLM technology requires systematic evaluation that extends beyond feature checklists to address implementation requirements, long-term viability, and organizational fit.
Essential technical capabilities include sophisticated document versioning that addresses parallel review processes and approval workflow integration, comprehensive metadata management supporting both structured taxonomies and flexible classification schemes, and robust search functionality accommodating complex queries across document content and metadata while maintaining security controls.
User experience significantly impacts adoption success. Effective interfaces reduce cognitive load while providing comprehensive functionality through progressive disclosure and contextual guidance. Workflow optimization should accommodate natural document handling patterns while enforcing compliance requirements transparently. Mobile accessibility increasingly affects user satisfaction as remote work requires document access from various device types.
Vendor evaluation criteria should address stability through financial health and market position assessment, implementation support quality through methodology maturity and change management assistance, and compliance expertise demonstrated through certifications and case studies. Reference customers provide valuable insights into real-world system performance and vendor support quality.
Building Your Implementation Strategy
Successful CDLM implementation requires systematic planning that addresses technical configuration, organizational change management, and performance measurement.
Current state assessment provides the foundation through comprehensive evaluation of existing document management practices, regulatory requirements, and organizational readiness. Gap analysis compares current capabilities against regulatory requirements and industry best practices to identify specific areas requiring attention.
Stakeholder engagement ensures implementation planning addresses diverse organizational needs through collaborative requirements gathering. Key stakeholders should include document creators, reviewers, compliance officers, and IT personnel.
Change management considerations address the human factors determining implementation success. Communication planning ensures stakeholders understand implementation objectives and timelines through targeted messaging. Training programs provide comprehensive skill building through multiple delivery methods, while support systems ensure users receive ongoing assistance.
Performance measurement frameworks establish clear criteria for evaluating implementation success through metrics aligning with operational objectives and regulatory requirements. Efficiency metrics track improvements in document handling speed and workflow completion times. Quality indicators measure document accuracy and compliance adherence. User satisfaction assessments gauge adoption success while compliance metrics demonstrate regulatory adherence through audit readiness indicators and violation reduction.
FAQ: Common CDLM Challenges
- Q: What is Compliance Documentation Lifecycle Management?
Compliance Documentation Lifecycle Management (CDLM) is the systematic approach to creating, maintaining, and preserving regulatory documents throughout their entire operational lifespan. It encompasses five critical phases: creation and authoring, metadata assignment and classification, storage and access management, retention and archival, and validation and audit support. - Q: How can organizations address version control challenges?
Implement standardized naming conventions embedding metadata directly into file names, deploy automated numbering systems preventing conflicts, and establish check-in/check-out procedures preventing simultaneous editing. Modern CDLM systems should integrate electronic signature capabilities complying with regulations like 21 CFR Part 11 while providing clear evidence of reviewer identity and approval scope. - Q: What metadata elements are most critical for regulatory compliance?
Essential metadata typically includes creator, creation date, document type, regulatory framework, approval status, retention period, and classification level. Industry-specific extensions address particular needs – pharmaceutical companies require drug substance information, while manufacturing organizations need product line and safety classification data. - Q: How should organizations evaluate cloud versus on-premise deployment?
Cloud deployment offers automatic updates, scalability, and reduced IT overhead, with major providers maintaining compliance certifications for SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GxP. However, some frameworks impose geographic restrictions or require direct organizational control. Hybrid approaches increasingly provide optimal balance, keeping critical documents on-premise while leveraging cloud scalability for less sensitive materials. - Q: How can AI improve compliance documentation processes?
AI applications include predictive analytics identifying compliance risks before violations occur, intelligent document generation producing drafts incorporating current requirements, and automated content review flagging potential issues. Natural language processing enables automatic extraction of regulatory references while machine learning suggests appropriate metadata values. Organizations typically see tagging accuracy improve significantly within the first year. - Q: What ensures audit readiness through CDLM systems?
Audit readiness requires comprehensive document inventories organized by regulatory framework, traceability mapping demonstrating relationships between documents and business processes, and automated evidence compilation responding efficiently to regulatory inquiries. Regular mock audit exercises test system responsiveness while identifying potential bottlenecks. Systems should provide secure auditor access and automated reporting generating standardized compliance reports.
Effective CDLM transforms regulatory documentation from a compliance burden into a strategic advantage supporting operational excellence while ensuring regulatory adherence. Organizations that invest in comprehensive CDLM capabilities position themselves for success in increasingly complex regulatory environments while building competitive advantages through operational efficiency and audit readiness.
Experience the Future of ESG Compliance
The Compliance & Risks Sustainability Platform is available now with a 30-day free trial. Experience firsthand how AI-driven, human-verified intelligence transforms regulatory complexity into strategic clarity.
👉 Start your free trial today and see how your team can lead the future of ESG compliance.
The future of compliance is predictive, verifiable, and strategic. The only question is: Will you be leading it, or catching up to it?
Simplify Corporate Sustainability Compliance
Six months of research, done in 60 seconds. Cut through ESG chaos and act with clarity. Try C&R Sustainability Free.