the business case
Corporate Sustainability Compliance
Compliance isn’t just about risk mitigation – it’s a lever for growth, valuation, and competitive advantage.
These metrics make it clear: ESG is now a boardroom priority, not a back-office function.
1533
ESG regulatory changes in the first half of 2025
82%
C-Suite execs see ESG as a business driver
+4%
Average increase in firm value from material ESG focus
5%
Global turnover in fines under CSDDD
Sustainability Regulatory Content
Built for corporate sustainability, with deep coverage across 8 ESG pillars.
The ESG Regulatory Brain for Your Business
One system that knows what applies, what matters, and what to do next.
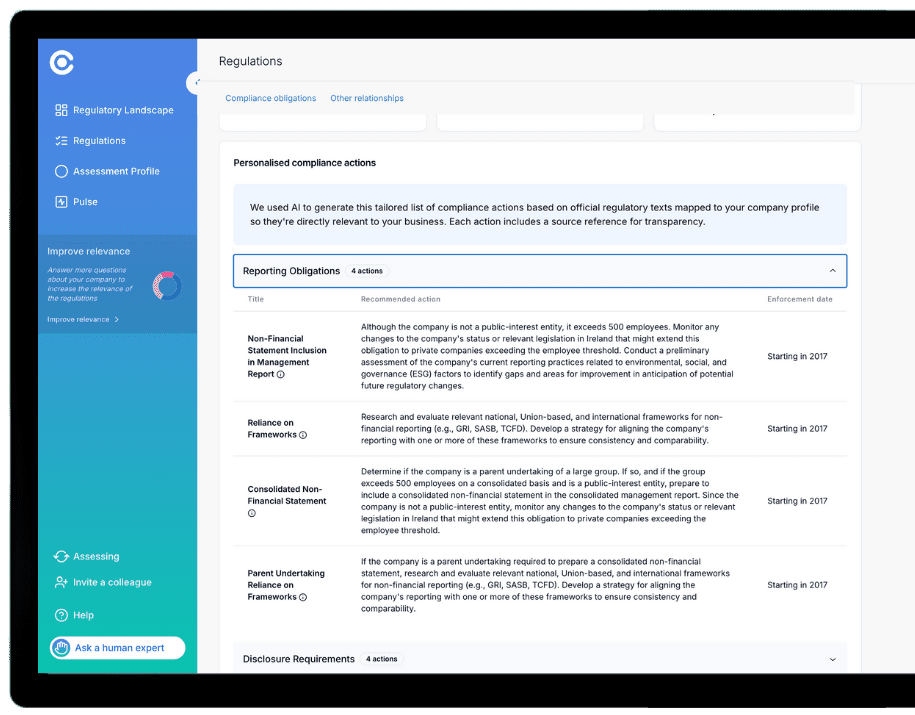
Regulation Summaries That Matter
Highlights the essential information in every regulation so teams can easily understand what’s important without spending hours reading legal text.
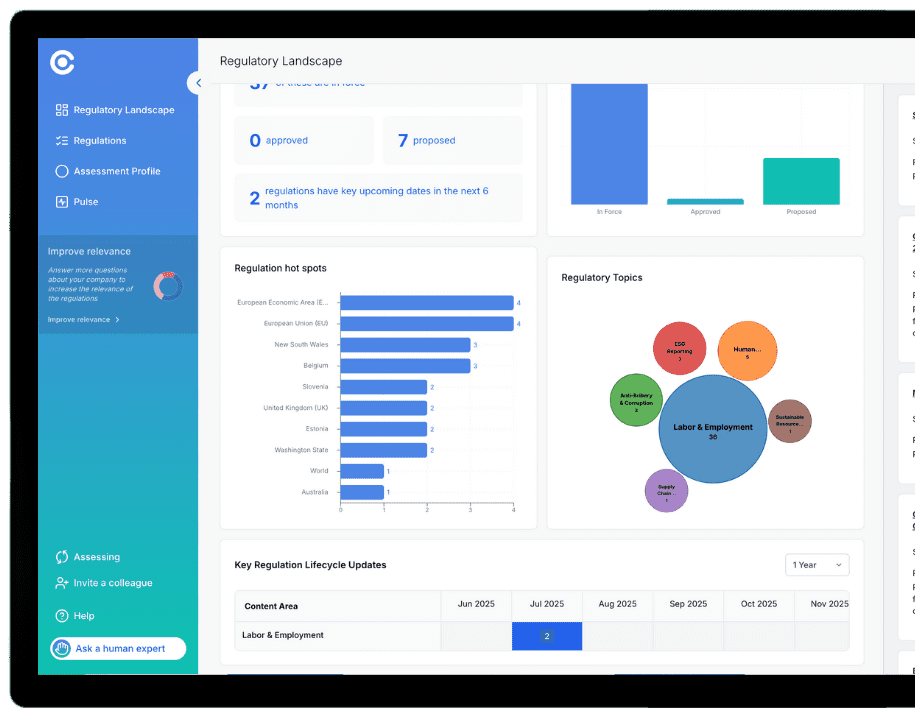
Regulatory Landscape View
Provides a real-time, dynamic dashboard of global regulatory activity: what’s in force, approved, and proposed.
Collaborative Compliance Workspace
Users can invite collaborators, share regulatory records, and add comments, ensuring alignment across the enterprise.
Manual Relevance Controls
Enables users to adjust or confirm AI-determined relevance of regulations based on internal policy, risk profile, or expert judgment.
Natural Language Search
Empowers users to quickly locate regulations using everyday terms or approximate names. No legalese required.
Fastest, Easiest Onboarding in the Compliance Industry
Get meaningful output in your first session. Zero implementation lag.
FAQ’s
What is ESG Compliance?
ESG compliance refers to the measures an organization takes to meet the environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards and requirements set by regulatory bodies and industry organizations. ESG compliance involves the reporting and disclosure of an organization’s ESG performance, policies, and practices in order to provide stakeholders with relevant and reliable information.
The purpose of ESG compliance is to ensure that organizations are accountable for their impact on the environment, society, and governance, and to encourage them to adopt sustainable business practices. ESG compliance can also help organizations to manage risks, improve their reputation, and enhance their relationships with stakeholders.
Check out our blog on ESG Compliance to learn about ESG Compliance in detail and how you can get started on your ESG journey.
ESG Compliance vs Sustainability Reporting: What’s the Difference?
As companies become more aware of their impact on the environment and society, they are looking for ways to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices. Two terms that are often used in this context are ESG compliance and sustainability reporting. But what do these terms mean, and what’s the difference between them?
ESG Compliance
ESG compliance refers to the standards that companies must meet in order to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices. This encompasses a wide range of issues, including environmental protection, human rights, labor standards, governance, and ethical behavior. Companies must adhere to these standards in order to maintain their reputation, reduce risk, and attract investment.
Sustainability Reporting
Sustainability reporting, on the other hand, refers to the process of disclosing information about a company’s environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. This can include information about a company’s carbon footprint, waste generation, labor practices, governance practices, and more. The goal of sustainability reporting is to provide stakeholders with a clear and transparent picture of a company’s ESG performance and to demonstrate a company’s commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices.
In summary:
ESG compliance is about meeting requirements, while sustainability reporting is about providing information.
ESG compliance is often mandatory, while sustainability reporting has been mandatory in the EU with the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) mandated under that Directive. Note that the EU Directive requires certain large & listed companies to publish regular reports on the social and environmental risks and how their activities impact the stakeholders and environment.
ESG compliance focuses on minimum standards, while sustainability reporting can provide a more comprehensive picture of an organization’s sustainability efforts.
In conclusion, both ESG compliance and sustainability reporting are important for companies looking to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices. ESG compliance is necessary in order to avoid penalties and fines, while sustainability reporting is focused on building a company’s reputation and providing stakeholders with information about its ESG performance. By taking both ESG compliance and sustainability reporting seriously, companies can reduce risk, attract investment, and build trust with stakeholders.
Is ESG compliance a mandatory/legal requirement?
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are a set of non-financial criteria that are used to assess the sustainability and ethical impact of a company. ESG considerations can include a company’s carbon emissions, labor practices, human rights record, and governance structure, among others. While there is no global standard for ESG compliance, many companies are taking steps to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices and ethical behavior. This can include publishing annual ESG reports, setting sustainability targets, and engaging with stakeholders to address ESG risks and opportunities.
Although ESG compliance is not a legally binding requirement in most countries, it is increasingly becoming a factor that investors, consumers and stakeholders consider when evaluating companies. Some countries, such as France, have introduced laws requiring certain disclosures of ESG information, but there is no comprehensive global legal framework for ESG compliance. However, companies may face reputational and financial risks if they do not address ESG issues, and there is a growing expectation among investors and the public that companies will demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices.,
Despite the lack of a comprehensive legal framework for ESG compliance, there is growing pressure from investors, consumers, and the public for companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable and ethical practices. This pressure has been fueled by increasing awareness of the impacts of climate change, human rights violations, and corporate governance failures. As a result, ESG compliance is becoming increasingly important for companies looking to build trust, secure funding, and maintain a strong reputation.
By using an ESG SaaS solution, companies can demonstrate their commitment to sustainable and ethical practices and improve their ESG performance over time. Additionally, a SaaS solution can help companies save time and resources by automating data collection and reporting processes, while providing real-time insights into ESG performance to support decision-making.
What is Materiality Assessment?
A materiality assessment is a process that companies use to determine which ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) issues are most relevant and impactful to their business and stakeholders. This involves considering both the potential positive and negative impacts of ESG issues on a company’s operations, reputation, and financial performance, as well as the expectations and concerns of stakeholders such as customers, investors, employees, and communities.
A materiality assessment helps companies prioritize their ESG efforts and determine what information they should report on, both to meet regulatory requirements and to provide stakeholders with relevant and meaningful information. The results of a materiality assessment also inform a company’s ESG strategy, helping it to identify areas for improvement and set achievable goals.
What is Double Materiality?
Double Materiality is a requirement for companies to report both on how sustainability issues affect their performance, position and development (the ‘outside-in’ perspective) and on the impact that the company has on people and the environment (the ‘inside-out’ perspective).
Overall, a materiality assessment is an important step in the ESG reporting process, helping companies to ensure that their reporting is focused, relevant, and valuable to stakeholders.
Is there an ESG compliance checklist?
Yes, there is an ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) checklist that companies can use to help ensure that they are covering all the important areas of ESG in their reporting. The specific items on an ESG checklist can vary, but typically include the following:
Environmental: Information on energy usage, emissions, waste, and water management, as well as climate-related risks and opportunities.
Social: Information on human rights, diversity and inclusion, labor practices, and community engagement, as well as other topics related to a company’s social impact.
Governance: Information on the company’s governance structure, risk management, and anti-corruption policies, as well as compensation and remuneration practices.
Financial: Information on the financial performance and sustainability of the company, including the impact of ESG factors on the bottom line.
The ESG checklist is not meant to be exhaustive, and companies may need to include additional items that are specific to their operations and stakeholders. Additionally, the specific ESG reporting requirements will vary depending on the jurisdiction, industry, and company size. However, an ESG checklist can be a useful starting point for companies looking to ensure that they are covering all the important areas in their ESG reporting.
Which ESG compliance framework should my company follow?
The choice of ESG compliance framework that your company follows depends on several factors, including the industry, location, and goals. Some of the most widely recognized ESG compliance frameworks include:
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): A globally recognized sustainability reporting framework that provides guidelines for companies to report on their ESG performance.
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB): A non-profit organization that provides industry-specific ESG reporting standards to help companies communicate their ESG performance to investors.
- Integrated Reporting Council (IRC): An international organization that provides guidelines for integrated reporting, which combines financial and non-financial information to provide a comprehensive view of a company’s performance.
- Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): A task force established by the Financial Stability Oversight Council that provides guidelines for companies to disclose information on the impact of climate risks and opportunities on their financial performance.
Ultimately, your choice of ESG compliance framework will depend on the specific needs and goals of your company.
It is recommended that companies consider the different frameworks and seek guidance from ESG experts to determine which one is the best fit for their needs.
What are ESG compliance requirements?
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) compliance requirements vary by jurisdiction and industry, but some common requirements include the following:
Environmental regulations: Companies must comply with environmental laws and regulations related to issues such as emissions, waste management, and conservation of natural resources.
Labor laws: Companies must comply with labor laws and regulations related to issues such as minimum wage, working hours, health and safety, and non-discrimination.
Corporate governance: Companies must comply with regulations related to corporate governance, including the disclosure of accurate financial information, the independence of directors, and the protection of shareholder rights.
Human rights: Companies must respect and uphold human rights, including those related to freedom of expression, privacy, and equality.
Sustainability reporting: Companies may be required to report on their ESG performance and initiatives, including their environmental impact, labor practices, and governance structure.
It is important for companies to stay informed of the evolving ESG compliance requirements in their jurisdiction and industry, as they can change over time. Companies can also consider adopting voluntary standards and guidelines, such as the Global Reporting Initiative or the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board, to demonstrate their commitment to ESG.
Who does ESG reporting apply to?
Large companies: Mandatory ESG reporting currently only really applies to companies above a certain threshold in terms of revenue and/or number of employees. For example, in the EU, the CRSD applies to:
(i) all companies listed on EU-regulated markets;
(ii) “Large” unlisted EU companies not listed i.e., companies exceeding at least two of the following on two consecutive annual balance sheet dates:
- €20 million total assets:
- €40 million net turnover (revenue)
- 250 employees during fiscal year:
(iii) EU companies that are a parent of a “large group” i.e., a group consisting
of parent and subsidiary entities and which, on a consolidated basis, exceeds at least two of the metrics outlined above.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting can apply to companies of all sizes and industries, although the exact scope and requirements can vary depending on the company’s size, location, and sector.
Publicly traded companies: ESG reporting is becoming increasingly mandatory for publicly traded companies, as investors and the public are increasingly interested in the ESG performance of companies they invest in or buy goods and services from.
Small and Medium-Sized companies (SME’s): While ESG reporting is not yet mandatory for SM’s in the EU, many are voluntarily choosing to report on their ESG performance in order to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable and ethical practices. It is worth noting that EFRAG is currently reviewing the potential development of a voluntary sustainability reporting standard for non-listed small and medium-sized undertakings that fall outside the scope of the CSRD
Non-profit organizations: ESG reporting is also becoming increasingly common for non-profit organizations, as they look to demonstrate their impact and build trust with stakeholders.
In some cases, ESG reporting may become mandatory for companies operating in specific industries only. There are several regulatory proposals in existence at present that, if enacted, would require certain manufacturers in the apparel and textile industry with net turnovers above a certain threshold to disclose their environmental due diligence policies and processes as well as targets for prevention and improvement.
It’s important to note that the requirements for ESG reporting can vary by country, region, and industry, and it is recommended to seek the guidance of a professional to understand the specific reporting requirements for your company.
Our team of subject matter experts are on hand for any queries you have on this matter. Talk to us and we will help find the right guidance for you.
How to implement ESG in a company?
Implementing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) practices in a company involves the following steps:
- Develop an ESG strategy: Establish the company’s goals and priorities related to ESG and create a plan to achieve them.
- Assess performance: Conduct a thorough assessment of the company’s current ESG performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Engage stakeholders: Engage with stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, and shareholders, to understand their ESG expectations and how the company can better meet those expectations.
- Integrate ESG into operations: Incorporate ESG practices into the company’s operations and decision-making processes. This can include reducing emissions, improving labor practices, and adopting ethical governance practices.
- Report performance: Report the company’s ESG performance regularly and transparently. This helps build trust with stakeholders and increases accountability.
- Continuously monitor and improve: Continuously monitor and evaluate the company’s ESG performance and make improvements where necessary to ensure the company is meeting its ESG goals and expectations.
How can my company stay compliant with all the upcoming ESG regulations?
To stay compliant with upcoming ESG regulations, your company can take the following steps:
- Conduct regular assessments:
Regularly assess the company’s ESG practices and policies to ensure they are in line with the latest regulations. - Develop a robust ESG management system:
Establish clear processes and systems for managing ESG risks and ensuring compliance with regulations. This includes setting ESG goals and regularly monitoring progress towards these goals. - Engage with stakeholders:
Engage with key stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors, and regulators, to understand their expectations and concerns regarding ESG regulations. - Seek expert advice:
Consult with ESG consulting firms or legal advisors who can provide up-to-date information on the latest ESG regulations and best practices. - Disclose ESG information:
Ensure that your company is transparent and accurately disclosing information about its ESG performance and practices. This includes reporting to relevant industry organizations and regulatory bodies. - Continuously educate and train employees
Regularly educate and train employees on the latest ESG regulations, as well as the company’s policies and practices.
By taking these steps, a company can stay compliant with ESG regulations and demonstrate its commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices.
How can I see a full picture of ESG regulations coming down the line?
C2P gives you a full picture of what is coming down the line, particularly with regard to proposed compliance deadlines and other proposed requirements in draft ESG sources. In general, to stay informed on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) regulations, you can follow the following steps:
- Subscribe to a reputable regulatory monitoring and tracking solution: Stay up to date with key ESG regulatory developments in force and coming down the line.
- Follow industry news: Stay updated on industry news related to ESG and look out for any new regulations or guidelines being proposed or implemented.
- Stay connected with industry organizations: Organizations like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) can provide valuable insights into the latest ESG regulations and best practices.
- Attend conferences and events: Participate in industry conferences and events that focus on ESG and sustainability to learn about the latest regulations and trends.
- Consult with experts: Consider seeking advice from ESG consulting firms or legal advisors who can provide you with up-to-date information on the ESG regulations relevant to your industry.
How do I set an ESG strategy for my company?
Setting an ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) strategy for your company involves the following steps:
- Assess your company’s current ESG performance
Review the company’s existing ESG initiatives, practices, and policies, and gather data on its ESG impact. - Define ESG goals and targets
Based on the company’s current ESG performance and the expectations of stakeholders, establish specific, measurable, and time-bound goals and targets for the company’s ESG performance. - Integrate ESG into business strategy
Incorporate ESG considerations into the company’s business strategy and ensure that ESG goals are aligned with the company’s overall mission and goals. - Establish a governance framework
Put in place an ESG governance structure that defines roles and responsibilities, establishes reporting and monitoring processes, and sets up systems for continuous improvement. - Communicate ESG initiatives
Clearly communicate the company’s ESG strategy, goals, and achievements to stakeholders, including investors, employees, customers, and the public. - Implement and monitor
Implement the ESG strategy by taking concrete actions and regularly monitor and report on the company’s ESG performance, and make changes as needed. - Continuously improve
Continuously review and improve the company’s ESG strategy and performance in response to changes in the business environment and stakeholder expectations.
Take the first step towards a more sustainable future for your business with our innovative SaaS ESG solution. See for yourself how our platform can help you track and improve your ESG performance, meet stakeholder expectations, and stay ahead of the competition.
Book a demo today and discover how our solution can help you achieve your ESG goals. Simply click the link below to schedule your demo at a time that works best for you. Don’t miss this opportunity to learn about the latest technology and best practices in ESG management!